Metallurgical Analysis.
Manganese Determination Method.
Determination Of Manganese in Silico Manganese, Ferro Manganese and its ores etc.
Economically feasible and effective determination of manganese by the volumetric (Volhard) method of chemical analysis in minimum time.
......by Sp Shende. India.
We are metallurgical analyst having more than 15 years experience. We do daily analysis of Mn, Si, Fe, MnO, SiO2, Al2O3, CaO, MgO, P, C, S and coke, coals FC 's etc. It's our daily work in our Laboratory. Out of this, we now see the "Method of determination of Manganese " i.e. "How to find out Manganese ? " and Silico manganese, Ferro manganese metals and it's ores etc.
In our Lab, we used three methods for finding out manganese as :
01.Fusion method. 02. Nitric-HF baking method. 03. Aquargia baking method.
Selection of method depending on your requirement and sample inspecting experience. Let we discuss herewith all of these three baking method with common volhard titration method for determination of Mn.
We always find out Manganese through this procedure daily in our Laboratory. With using this method, you can find out Manganese within four hours. Several metallurgical chemist comes in our laboratory and learn, applied and compared to standard Lab Samples results in their labs. And agreed that It's a perfect method to find out manganese in minimum time !
After applying this method, your search for 'How to Find out Manganese ' ends here !
Let we explain this genuine research and experience method for Determination of Manganese step by step here. Let's Start now !
01. As per your requirement, Take crushed and 100 mesh fine powder of Silico manganese or Ferro manganese or Ore sample. And dry this sample in oven at 105 degree centigrade for one hour. And keep it aside to attain a room temperature (27 – 30 degree centigrade).
02. Baking Process :-
Depending on your requirement, You may use any one of baking process for finding out Mn in Metal and ores samples as :
A. Baking with HF : for finding out Mn, Fe
B. Baking with Aquargia : for finding out Mn, Si, Fe, and P
C. Baking after fusion. : for finding out Mn, Si
Choice is yours !
A. Baking with HF :- Take 0.5gm or 01gm oven dried moisture free sample of metal or ore, in 500ml- glass beaker. And add 35 ml Concentrated Nitric Acid (HNO3) in it. Place it on hot plate. After warm, add drop by drop Concentrated Hydrofluoric (HF) acid in it, until the vigorous reaction has subsided. (it takes 5 ml HF approx.). Remain it on hot plate.
B. Baking with Aquargia ( HCL : HNO3 | 03 : 01 ) :- Take 0.5gm or 01gm oven dried moisture free sample of metal or ore, in 500ml-glass beaker. : Add 30 ml Concentrated Hydrochloric Acid (HCL) in it, And then add 10 ml concentrated Nitric Acid (HNO3) in it. Place it on hot plate.
C. Baking after Fusion :
For this, initially fusion process is carried out as :
Fusion process :-
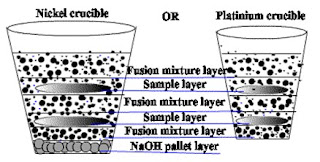
Take 0.5gm or 01gm oven dried moisture free sample of metal or ore, in Nickel Or Platinum crucible, with fusion Mixture. Layers of sample and fusion mixture is shown in following fig.1
If you used Nickel crucible, then initially thin NaOH layer should be kept at the bottom of Nickel crucible.
Thin fusion mixture layer is added firstly at the bottom of platinum crucible.. After that, approx. half quantity of your weighted sample’s layer is added, and then cover it with adding fusion mixture layer. Again remaining half quantity of your weighted sample’s layer is added, and then cover it with adding fusion mixture layer. Cover the crucible with lid. Fuse it in Muffle furnace as :
I. Initially, Set the Muffle Furnace Temperature controller’s settings at 800 degree centigrade. And wait for achieving 800 degree C. temperature by Muffle furnace. After achieving approx. 800 degree centigrade by Muffle Furnace : Heat crucible first gently, and insert it into the Muffle furnace having initially temperature at approx. 780 to 800 degree centigrade.
II. Then after inserting crucible : Set the Muffle furnace Temperature Controller’s setting at 910 degree centigrade. And wait for achieving 900 temperature by Muffle furnace. After achieving 900 degree centigrade by Muffle Furnace : Remain crucible in it for approx. 05 to 07 minutes.
And after approx. seven minutes, withdraw the red hot crucible from Muffle furnace.
III. Keep the red hot crucible in vertical position : Slowly revolve crucible roundly until the melt in crucible starting become towards thick.
Then After : Slightly inclined crucible and slowly rotate it in such a manner that, the melt in crucible spreads on the all sides of the crucible. After uniformly spread melt on the all sides of the crucible, keep it aside to attain room temperature(27-30 degree C).
IV. Take 400ml capacity glass beaker : Add 40ml distilled water in it. And then add 40 ml concentrated Hydrochloric acid (HCL) in it. Place it on hot plate. And insert your above fused and cool crucible in that beaker. Remain it on hot plate up to completely extraction the crucible’s solid melt into the beaker solution. After completely extraction of melt in to the beaker : Withdraw crucible from beaker. Hold crucible above beaker’s mouth and wash this crucible with distilled water in such manner that no melt particles remains on crucible.
Add 25 ml excess concentrated HCL in above beaker solution and use it for further analysis.
Take any one of obtained solution by above three process : place it on hot plate. And evaporate it slowly up to entirely dryness. After dryness : Further remains it on hot plate for approx. 20 minutes for baking. This is call as baking process. This baking process takes approx. 60 minutes.
03. Re baking :- Add approx. 20 ml Concentrated HCL in above beaker’s baked mass. Then again it evaporate slowly over a hot plate up to completely dryness. After dryness further bake it for approx. 10 minutes on hot plate.
04. Re dissolution :- After completed baking, take out baked and completely dried mass containing beaker, from hot plate. And cool it for five minutes at room temperature (27-30 degree C).
After 5 Minutes cooling, now add 40ml Concentrated Hydrochloric (HCL) in that residue, and again place it on hot plate until the HCL quantity becomes Half (i.e. up to 20ml).
After half quantity reduction of Concentrated HCL, now add approx. 20ml distilled water in it, so that the quantity become again aprrox. 40ml in beaker. And again remains it on hot plate until the quantity becomes again half ( i.e. approx. 20ml).
This approx. 20 to 15ml solution is your pasty mass residue solution. This redissolved pasty mass residue solution making process, is called as Redisolvetion process. This re disolvetion process takes approx. 40 to 50 minutes.
05. Filtration :- Take out beaker containing redissolved residue, from hot plate. And add approx. 15ml distilled water in it. Filter it through 41 No. Whatman's filter paper. Wash it 02 to 03 times by warm distilled water
Keep in mind that : In filtration process, take the filtrate solution in 250ml-Volumeric flask.
After completing filtration process : Take filter paper collected ppt. for further analysis of Si determination process. For Mn determination take filtrate for further analysis.
Make up filtrate solution up to 250 ml mark level of volumetric flask, by adding distilled water in it. Allow the content of the flask to settle. Cool it well and check mark level of volumetric flask again. After cooling : If solution level goes below the mark level of volumetric flask, then add drops of distilled water up to mark level of volumetric flask. Shake and mixed it well for further analysis
Remember that : If you take 0.5gm sample for analysis, and make up it into 250ml Volumetric flask, then 0.1gm quantity of sample is pipette out as 50ml for your titration process. And if you take 01 gm sample for analysis, and make up it into 500ml Volumetric flask, then 0.1gm quantity of sample is pipette out as 100ml for your titration process.
06. Titration process :- Pipette out 50 ml filtrate solution (0.1gm), from above 250ml-volumetric flask. Take this pipette out 50 ml solution into a 500ml-conical flask. Dilute this 50ml solution by adding 200ml distilled water in that conical flask..
07. Boil this 250ml solution about a minutes for removing free chlorines, salts etc. and then keep it aside to attain a temperature 80 degree centigrade .
Note :- If you are using Tab water for analysis, then take 200ml Tab water in flask and boil it about 04 minutes firstly. It is necessary because tap water contains bleaching, free chlorine etc. salts. Hence boil 200 ml Tap water for 2 to 4 minutes for removing free chlorine, bleaching etc. salts. And then add 50 ml filtrate solution in it. And boil it for a minutes.
Shake and keep it aside to attain a 80 degree centigrade temperature of solution in flask. .
08. After attaining approx. 80 degree centigrade : add small amounts of Zink Oxide (ZnO) powder in that solution, until a point is reached where the liquid suddenly coagulates, precipitating all the iron of the solution.( It can be judged by the presence of undissolved ZnO powder at the bottom of flask)
Add excess one teaspoon ZnO powder in it for Milky white color.
Keep in mind that : ZnO powder only react with iron ions, it does not affect on Mn ions. Hence little excess addition of ZnO powder is permissible.
09. Again heat this coagulated milky white precipitate solution up to the boiling point. ( approx. 98 degree centigrade : avoid boiling ) then add 5ml 50%HNO3( 1 : 1 ) in it. Remember that : Addition of 05ml 50%HNo3(1:1) acid causes the subsequent precipitate to settle down quickly. Shake and down it’s temperature up to 90 to 80 degree centigrade.
10. Titrate this approx. 90 to 80 degree centigrade solution with (0.1 N) KMnO4 solution up to the color changes to light pink color. When light pink color appears in liquid, bring the contents of flask nearly to boiling point( approx. 80 to 95 degree centigrade, avoid boiling as it may destroy the permanganate coloration.) once more. And again observe that : The pink color tint still persist in solution. If pink color vanishes, then addition of permanganate solution is necessary up to the existence of permanent light pink color.
Take Burette Reading at permanent light pink color, which is your end point of titration process.
Keep in mind : During titration process, maintain titratration temperature between. 90 to 80 degree centigrade. And avoid boiling, as it may destroy the permanganate coloration.
Remember that, In titration process :
I. The permanganate may causes a precipitate which .clouds the liquid and it is therefore necessary to titrate cautiously and agitate the flask after each addition of KMNO4. And then allow the precipitate to settle sufficiently to observe whether or not the solution has taken light pink color. While observing the light pink color end point, if the conical flask is kept in a slanting position on stand, then it can be easily observed.
II. The titration is made as possible as quickly and the solution in flask is not allowed to cool below 80 degree centigrade during titration process. For achieving this : you have to do two titration. Titrate firstly to find out approx. BR end point. And at the second titration, add KMNO4 quantity slowly up to one point below the first titration BR reading end point. While adding approx. first BR reading quantity of KMNO4, agitate and shake flask continuously. And find out final accurate BR end point in your second titration.
III. In titration : Each drop of (0.1N) Kmno4 causes the formation of manganous acid(H2MnO3). Under ideal condition, reaction may takes place as :
2 KmnO4 + 3 MnSo4 + 7 H2O = 5 H2MnO3 + K2So4 + 2H2So4
Each 01 ml Of (0.1N) KMnO4 solution, react with approx. 0.001666gm of Mn. Hence the actual formulas for Mn is derived as :
%Mn = [ BR x 0.001666 x N ] x 100 ➗ weight of Sample Taken in gm for titration
± standard Difference error
But chemist always takes 0.1gm for titration, hence above formula is simplified as :
%Mn = BR x 1.666 x N ± standard Difference error
12. Manganese Formulas :-
% Mn = [ (BR) x 1.666 x N ] ± standard Difference error
Where
% Mn = Manganese percentage%
BR = Burette Readings. (End point reading of titration.)
N = Normality of KMNO4 solutions.
± Standard Difference error :-
By the above procedure, find out manganese of standard Sample and its difference.
e.g. If standard sample Known manganese is 60 %, and by above procedure that standard sample manganese comes as 60.5 %, then standard difference is 60-60.5 = 0.5 is subtracted as standard difference error in your above procedure result.
Remember that : Whenever you makes any new solutions required for above procedures, you must find out first Standard difference using standard Sample.
In general practice : Seller side experienced analyst keep approx. 0.4 to 0.5% result in their own hands, to avoid the dispute between sellers and buyers dealings.
For example : If seller side well experienced chemist’s result comes as Mn = 60.50% , then he gives the result as “Result x 0.5% -less”. Thus he gives his result as 60.50 - 0.30 = 60.20% : by keeping 0.30 in his hand, to avoid disputes between two parties.
Precision of the method < 0.5 %
Chemicals Required for Manganese Procedures : -
01. Nitric acid ( HNO3) min 69% GR grade Merck or equivalent.
02. Hydrochloric acid (HCL ) ) min 35% GR grade Merck or equivalent.
03. Hydrofluoric acid (HF ) about 40% HF GR grade Merck or equivalent.
04 ZnO powder
05. Potassium per Manganate ( KMnO4 ) powder GR grade. Merck or equivalent.
OR N/10 Potassium per Manganate ( KMnO4 ) standard solution(0.1N) ampoules.
06. Oxalic acid purified M=126.07g/mol. Merck or equivalent.
OR Di-Sodium Oxalate(Na2C2O4) purified M=134.00g/mol. Merck or equivalent.
07. Sodium Carbonate anhydrous pure (Na2Co3). Merck or equivalent.
08. Potassium Carbonate(K2Co3) pure. Merck or equivalent.
09. Sodium Peroxide granular GR grade. Merck or equivalent.
10. Whatman filter papers ashless No.41 ( 125mm φ x 100 circles. Cat. No. 1441-125 )
Whatman filter paper qualitative No.1 ( 125mm φ x 100 circles. Cat. No. 1001-12 )
Solutions made by using above chemicals :-
Remember that : While making any solutions, Only use pure distilled water. Don't use tap water because tap water itself contains small amount of phosphorus, chlorine etc. salts, which affects your results.
How to check pure distilled water ?
Care should be taken that not a single drop of Tap water remains in your glassware. Hence wash 500ml-beaker by distilled water one or two times. And then take 100ml distilled water in that washed beaker. Add 0.5gm silver Nitrate crystals in it.
And observe that :
If white precipitate is not form, then it is pure distilled water.
If milky white precipitate forms, then that water is not a pure distilled water.
Solutions preparation :-
How to make KMnO4 Stock solution ?
Take 31.23gm KMnO4 crystalline powder in 05 liter capacity conical flask. Add 1.5 liter distilled water in it. Shake well and Place it on hot plate at 70 to 80 degree centigrade, up to the solution quantity reduced to half ( approx. 800 ml ). It takes approx. 16 to 24 hours.
After half Quantity reduction of solution on hot plate, again add 01 liter distilled water in it. And remains it on hot plate up to the reduction of 800 ml quantity. ( It takes again approx. 16 to 24 hours.)
Take out above 800 ml reduced solution from hot plate. In the funnel, add glass wool and filter this solution through glass wool. Wash glass wool 02 to 03 times with using distilled water.
Make up the filtrate solution up to exactly 01 liter. Store it in Amber bottle and place it at cool and dark place.
This KMnO4 Stock solution contains approx. 31.23 gm KMnO4 per liter. This Stock solution making process takes approx. 36 to 48 hours.
How to Make KMnO4 (0.1 N) solution from stock solution ?
Take 02 lit. capacity Conical Flask : Add 100ml above Stock solution, and 900 ml distilled water in it. Shake and mix it well. Give sufficient time to settle down and then filter it through 1.No Whatman filter paper. It may be your approx. Normality(0.1N) KMnO4 solution. For perfect Normality : Standardized this solution by checking Normality. and adding calculated ml. quantity of distilled water in it.
In general practice : If your prepared solution’s Normality is less than 0.1 N, then drops of distilled water is added to make it 0.1 N. Else if your prepared solution Normality is greater than 0.1 N, then drops of KMnO4 stock solution is added to make it as unity normality.
How to Make KMnO4 (0.1 N) solution from N/10 KMnO4 ampoules ?
As per instruction given on ampoules cover, Make the N/10 i.e.(0.1N) KMnO4 solution.
How to check Normality of KMnO4 Solution ?
There are different methods for finding out the normality of KMnO4. Out of this, Let we discuss some of them as :
I. Method for finding out Normality of KMnO4 solution, using Oxalic acid power :
Take 250 ml capacity volumetric flask : Add 02 gm Oxalic Acid powder in it, and add distill water up to the mark lever of 250ml Volumetric flask. Dissolve it by shaking well.
From this well 250ml Volumetric flask, pipette out 25ml solution(0.2gm) from it.
Take this 25ml solution in 500ml capacity beaker. And add 02 to 04 drops of concentrated Sulfuric acid (H2SO4). Then heat it up to boiling point temperature(approx 98 degree centigrade, avoid boiling)
Titrate this 90 to 80 degree solution against KMnO4 solution up to the light pink color which is your endpoint of titration. Take Burette Reading at end point.
Normality of KMnO4 Solution = [ (weight of sample taken for titration X 1000 ) ➗ equivalent weight of oxalic acid (63.035) ] ➗ Burette Reading(BR)
For example :- N = 0.2 x 1000 ➗ 63.035 ➗ 32 = 0.09915
II. Method for finding out Normality of KMnO4 solution, using Oxalic acid power :
Take 500ml capacity beaker : Add 0.1576 gm moisture free oxalic acid powder and 200 ml distilled water in it, and 04 to 06 drops of concentrated Sulphuric(H2SO4) acid in it. Stir it by using glass rod up to completely dissolved power.
Heat this dissolved powder solution up to 98 degree centigrade. Avoid boiling because it starts evaporation of oxalic acid.
Titrate this 90 to 80 degree solution with your prepared KMnO4 Solution up to the light pink color end point. Take Burette Reading at end point. Calculate normality as;
N = 25 ➗ Burette Reading of end point.
Note :- 126.07g/mol oxalic acid x 0.05 = 6.303gm oxalic acid per 1000ml KMnO4 solution => 0.1575gm oxalic powder per 25 ml KMnO4 solution.
III. Method for finding out Normality of KMNo4 solution, using Di-sodium Oxalate (D.S.O.) power :
Take 500ml capacity beaker : Add 0.1675 gm moisture free Di-sodium Oxalate(D.S.O) powder and 200 ml distilled water in it, and 04 to 06 drops of concentrated Sulphuric acid in it. Stir it by using glass rod up to completely dissolved power.
Heat this dissolved powder solution up to 98 degree centigrade. Avoid boiling because it starts evaporation of Di-sodium Oxalate.
Titrate this 90 to 80 degree solution with your prepared KMnO4 Solution up to the light pink color end point. Take Burette Reading at end point. Calculate normality as;
N= 25 ➗ Burette Reading of end point.
Note:- 134 g/mol D.S.O. powder x 0.05 = 6.70gm D.S.O. powder per 1000ml KMnO4 solution => 0.1675gm D.S.O. powder per 25 ml KMnO4 solution.
IV. Method for finding out Normality of KMnO4 solution, using Standard Sample :
Find out the Mn of a Standard Known Mn Sample with using your newly prepared KMnO4 Solution, by considering Normality as 01N ( Mn = BR x 1.666 x 1).
Normality of KMno4 Solution = Known Mn in Standard Sample. ➗ Actual Mn results of standard sample, considering Normality as one.
For example :- If your Known Standard Sample’s Mn is 60, and it’s actual Mn comes out as 60.50, then Normality of used KMnO4 solution = 60/60.50 = 0.9917 is normality of your used KMnO4 solution. Experienced chemist always used this method.
02. 50 % HNO3 ( 1 : 1 ) solutions :-
Take 100ml distilled water and add 100ml Concentrated HNO3 in it slowly.
shake and mixed it. pour it in dropper.
03. Fusion mixture :-
Sodium Carbonate anhydrous pure . : 02 parts
Potassium Carbonate(K2Co3) pure. : 02 parts
OR
Sodium Carbonate anhydrous pure . : 02 parts
Potassium Carbonate(K2Co3) pure. : 02 parts
Sodium Peroxide granular GR grade. 01 parts.
OR
Sodium Carbonate anhydrous pure . : 03 parts
Sodium Peroxide granular GR grade. 01 parts.
As per your requirement : Take the above combinations of powders, and mix it well. It is your Fusion Mixture.
Precaution :- Sodium Peroxide is explosively react with water. Keep it away from water. Also don't handle it with naked hand.
Labels :
Metallurgical Analysis by Sp Shende , Analysis of Manganese (Mn) , Silico Manganese , Ferro Manganese , Pearl Coke, Steme Coal, Charcoals, Volhard's method , (Mn) , Si , Fe , MnO , SiO2, Al2O3 , CaO, MgO, P, C, S, Fusion Mixture ,
Keywords :-
Metallurgical Analysis.
Metallurgical Analysis by Sp Shende.
Manganese Determination Method.
Determination Of Manganese.
Analysis of Manganese.
Determination Of Manganese by Sp Shende.
Determination Of Manganese in Silico Manganese.
Determination Of Manganese in Ferro Manganese.
Determination Of Manganese in Manganese ores.
Determination of Manganese by the Volhard's method.
Economically feasible and effective determination of Manganese
Method of chemical analysis of Manganese.
Method of chemical analysis of Manganese in minimum time.
Method of determination of Manganese.
Manganese finding procedures.
How to find out Manganese ?
How to find out Manganese within four hours ?
How to find out Manganese in minimum time ?
How to check pure distilled water ?
How to check Normality of KMnO4 solution ?
Method for finding out Normality of KMnO4 solution, using Oxalic acid power
Method for finding out Normality of KMNo4 solution, using Di-sodium Oxalate (D.S.O.) power
Method for finding out Normality of KMnO4 solution, using Standard Sample
How to make KMnO4 Stock solution ?
How to Make KMnO4 (0.1 N) solution from stock solution ?
How to Make KMnO4 (0.1 N) solution from N/10 KMnO4 ampoules ?
How to make N/10 Normality KMnO4 solution ?
How to make Fusion Mixture ?
Chemicals required for Manganese.
Solutions for Manganese.
Analysis of Mn, Si, Fe, MnO, SiO2, Al2O3, CaO, MgO, P, C, S
Finding out Fixed Carbon FC's of pearl coke, steam coals, Charcoals and its analysis.
Sp Shende , S. P. Shende , spshende , sp_shende, Sudan Prabhakar Shende.
Analysis Method contents written by :- Sp Shende.

Address :- Sp Shende. 64, Om Colony, ArniRoad, Yavatmal 445001 (M.S.) India.
Links of Other Metallurgical method’s contents submitted by Sp Shende :-
Metallurgical Analysis by Sp Shende.
Determination of Manganese (Mn).
Determination of Silica (Si).
Determination of Iron (Fe).
Determination of Phosphorus (P).
Determination of Sulphur (S).
Determination of Carbon (C).
Determination of Manganese dioxide ( MnO2)
Determination of Silica dioxide (SiO2).
Determination of Alumina (Al2O3).
Determination of CaO.
Determination of MgO.
Calculation of Basicity of Furnace.
Determination of Fixed Carbon’s (FC’S) of pearl coke.
Determination of Fixed Carbon’s (FC’S) of Steam Coal.
Determination of Fixed Carbon’s (FC’S) of Charcoals.
How to check PPM of water ?.
Thanks.
Metallurgical Analysis.
Metallurgical Analysis by Sp Shende.
Manganese Determination Method.
Determination Of Manganese.
Analysis of Manganese.
Determination Of Manganese by Sp Shende.
Determination Of Manganese in Silico Manganese.
Determination Of Manganese in Ferro Manganese.
Determination Of Manganese in Manganese ores.
Determination of Manganese by the Volhard's method.
Economically feasible and effective determination of Manganese
Method of chemical analysis of Manganese.
Method of chemical analysis of Manganese in minimum time.
Method of determination of Manganese.
Manganese finding procedures.
How to find out Manganese ?
How to find out Manganese within four hours ?
How to find out Manganese in minimum time ?
How to check pure distilled water ?
How to check Normality of KMnO4 solution ?
Method for finding out Normality of KMnO4 solution, using Oxalic acid power
Method for finding out Normality of KMNo4 solution, using Di-sodium Oxalate (D.S.O.) power
Method for finding out Normality of KMnO4 solution, using Standard Sample
How to make KMnO4 Stock solution ?
How to Make KMnO4 (0.1 N) solution from stock solution ?
How to Make KMnO4 (0.1 N) solution from N/10 KMnO4 ampoules ?
How to make N/10 Normality KMnO4 solution ?
How to make Fusion Mixture ?
Chemicals required for Manganese.
Solutions for Manganese.
Analysis of Mn, Si, Fe, MnO, SiO2, Al2O3, CaO, MgO, P, C, S
Finding out Fixed Carbon FC's of pearl coke, steam coals, Charcoals and its analysis.
Sp Shende , S. P. Shende , spshende , sp_shende, Sudan Prabhakar Shende.
Analysis Method contents written by :- Sp Shende.

Address :- Sp Shende. 64, Om Colony, ArniRoad, Yavatmal 445001 (M.S.) India.
Links of Other Metallurgical method’s contents submitted by Sp Shende :-
Metallurgical Analysis by Sp Shende.
Determination of Manganese (Mn).
Determination of Silica (Si).
Determination of Iron (Fe).
Determination of Phosphorus (P).
Determination of Sulphur (S).
Determination of Carbon (C).
Determination of Manganese dioxide ( MnO2)
Determination of Silica dioxide (SiO2).
Determination of Alumina (Al2O3).
Determination of CaO.
Determination of MgO.
Calculation of Basicity of Furnace.
Determination of Fixed Carbon’s (FC’S) of pearl coke.
Determination of Fixed Carbon’s (FC’S) of Steam Coal.
Determination of Fixed Carbon’s (FC’S) of Charcoals.
How to check PPM of water ?.
Thanks.